Launching a startup seems to be an existing one, but building a full-featured product right away can be risky, as it is a costly and time-consuming approach. That's where MVP development for startups comes in. A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the simplest version of your idea or project that focuses on building the core features and testing them with real users before investing heavily in development. It is the best approach to validate assumptions, reduce costs, and reach the market faster.
For entrepreneurs, MVP development for startups is not just a cost-saving measure but is a proven minimum viable product strategy that helps validate market demand, attract investors, and speed up business growth. According to Investopedia reports, 90% of startups without proper early-stage validation often fail, as there is no real-world market need for what they have built.
On a positive note, about 82% of successful startups began with a basic MVP software development instead of a fully developed product, as per stats. This shows how powerful a good minimum viable product strategy can be for early-stage product development. It also gives you feedback at an early stage and helps you learn what your customers actually want. Thus, you can modify or adjust the development instead of guessing and overbuilding.
What is an MVP in Startups?
An MVP, aka Minimum Viable Product, is the simplest version and is the process of testing your idea quickly and efficiently without overbuilding. The aim of this approach is to launch a basic version of your product, gather feedback from real users, and make improvements step-by-step. This approach begins with lean startup MVP principles and thus helps you save time and money. While testing your ideas quickly, it focuses only on the features customers really need.
For those founders who wonder, "What is an MVP in startups can think of it as your product's first functional version that lets you see if your solution is resolving the problems of the users. Instead of spending months creating a fully-featured product, an MVP allows you to find the demand, gather insights, and pivot faster if needed.
MVP Vs Other Product Development Strategies
Most often, when planning a product launch, startups often get confused between terms like PoC, Prototype, and Minimum Viable Product (MVP). Each of them serves different purposes from idea to market.
MVP - It is the process of testing whether the product meets actual market needs. It is designed to work with real users and thereby collect actionable feedback.
Proof of Concept (PoC) - This is all about testing whether an idea or technology is possible to implement technically. It is used internally.
Prototype - It is a visual or interactive model of your product that shows how it looks and works. However, it is not always fully functional and is helpful for MVP design and testing before actual development.
Check out the difference between the proof of concept vs MVP vs prototype in a tabular view:
| Approach | Purpose | Audience | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of Concept (PoC) | Tests if an idea or technology is technically possible | Internal teams | Confirms feasibility, no user testing |
| Prototype | Shows how the product might look and function | Stakeholders, early testers | Helps with MVP design and testing, collects feedback on usability |
| Minimum Viable Product (MVP) | Launches a simple, working product with core features | Real users | Validates demand, gathers insights, and guides the minimum viable product strategy |
Is MVP Outdated in 2026?
Some people believe that an MVP approach is outdated, as users are expecting a more polished product. However, in reality, MVPs are more relevant than ever. The key is to launch a usable, simple version of the product that solves the main problem effectively. Modern MVPs are designed to balance speed with user experience, making it a smart choice to custom software development for startups.
When to Use an MVP Vs a Full Product Build?
An MVP is best when you need to:
- Validate an idea before making a hefty investment.
- Get faster time to market.
- Collect real customer feedback for future updates.
A full product build is useful only after validating the demand, securing funding, or having clear proof that customers want advanced features. By starting with an MVP, you are eventually reducing risk and avoiding wasting resources on features that may be less useful.
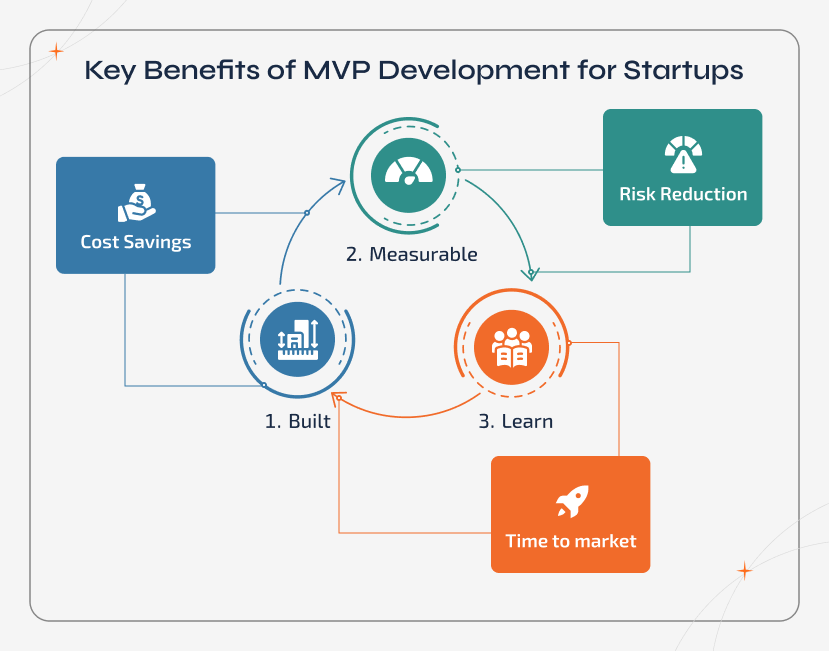
Key Benefits of MVP Development for Startups
For early-stage businesses, building MVP for startups is not just a shortcut. But it acts as a minimum viable product strategy that saves time, effort, money, and reduces risks while setting up the foundation for growth. Here are the main advantages of MVP development for startups:
1. Faster Product Validation with MVP
With an MVP, it is easy to test your idea in the real world instantly. Unlike traditional development, startups need not wait for months to launch a full product build. With MVP, a simple version can be launched, and validation can be carried out to check if it solves the problem faced by the customers.
2. Reduced Risks & Lower Investment
In many cases, startups fail due to too much investment in untested ideas. But with MVP development, companies can effectively minimize the financial risks by focusing only on core features. This approach ensures that the startups do not overspend on those features users may never need.
3. Cost-Effective MVP Solutions
Developing an MVP solution for startups is a far more cost-effective approach than building a full product upfront. Startups can save resources for scaling later by investing in a smaller version first, which is a very important factor for lean budgets.
4. Early User Feedback Loop
The iterative MVP development covers build, launch, learn, and improve. Getting early feedback from real users makes it easy for startups to refine their product. This ensures they are building something that is actually wanted by people.
5. Market-Fit Testing
An MVP acts as a launch strategy that can be used to measure product-market fit. By tracking usage patterns and feedback, startups can check if their idea resonates with customers before committing to a larger build.
Before You Build an MVP [Prerequisites Checklist]
Before you start developing, make sure the fundamentals are in place. This will possibly prevent wasted budget, wrong-product risk, and failed launches.
Problem & User Alignment
✅ Defined target user persona
✅ Clear problem statement
✅ Verified pain points
Lean Validation Setup
✅ Simple lean canvas Drafted (Problem, Users, Value proposition, Solution idea, Revenue logic & Cost structure)
MVP Format Selection
(Pick one of the below based on validation, not hype)
✅ Landing page MVP
✅ Concierge MVP
✅ Single-feature product
✅ Prototype MVP
User Access & Feedback Plan
✅ Identified early adopters
✅ Feedback channels planned
✅ Recruiting plan in place
✅ Iteration loop defined
✅ Beta user access
The Startup MVP Development Process - A Step-By-Step Guide
Most often, startup owners wonder how to structure an MVP, and the answer is to follow a clear, repeatable process that balances speed with learning. A well-planned startup MVP development process will be all about focusing on solving the right problems while avoiding unwanted effort. Here goes the step-by-step process breakdown:
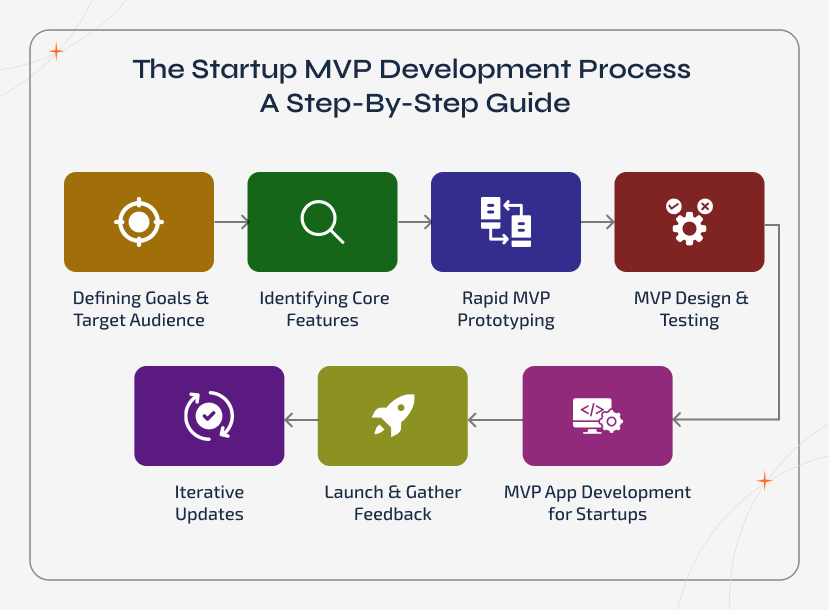
Step 1: Defining Goals & Target Audience
Every MVP starts with a clearly defined goal. i.e, it should define the problem your product is about to solve, your business goals, and the target users who will be benefiting. Without this solid foundation, your MVP will risk missing the mark.
Step 2: Identifying Core Features
The next step is to list down all the possible features and opt to work on only those essentials. i.e., the ones that directly solve the main problems of the users. This helps you stay lean and prioritize the values over complexity.
Step 3: Rapid MVP Prototyping
Before building the MVP, it is important to create quick wireframes and prototypes. This step ensures startups can visually check the idea, refine the user flow, and obtain early validation from the stakeholders or test users.
Step 4: MVP Design & Testing
Even for an MVP, a simple and intuitive design is an important factor. With usability tests, startups can check if users can navigate and use the product easily. This reduces the friction and ensures you are ready for the launch.
Step 5: MVP App Development for Startups
The next step upon validating is to move into development. It is vital to keep the development lightweight while focusing on the functionality. In most cases, many teams will adopt agile MVP development practices in this stage and thus ensure flexibility and faster iterations.
Step 6: Launch & Gather Feedback
During this phase, MVP gets released to a small set of real users. With this, their engagement is monitored, feedback will be collected, and a detailed analysis will be made to find if the product launched has solved their needs.
Step 7: Iterative Updates
Upon gathering the insights, the MVP development team will decide on improving and expanding the product for the startups step by step. This is the actual phase where MVP development seems helpful. The team will work on continuously adapting to the required features to achieve the product-market fit.
How Basic MVPs Launched Billion-Dollar Companies - Real-World Success Stories
Taking a look at real-world success stories shows how powerful a minimum viable product strategy can be for the top software development companies. There are a lot of global brands that started with small, simple MVPs before becoming successful, and the most popular examples are as follows:
1. Dropbox - Explainer Video MVP
Dropbox began with a simple explainer video rather than a fully built product. This MVP illustrated the app's concept and attracted lots of signups. This is seen as the validation of the demand before the entire product was even developed. This approach has helped Dropbox get secure funding and scale successfully.
2. Airbnb - Initial Landing Page Test
Airbnb's founder didn't create a full booking platform at the very beginning. Instead, they built a basic landing page to test if people would pay to stay in someone's place. When they saw real booking, they scaled the platform globally and are one of the most successful booking platforms in the global marketplace.
3. Spotify - Limited Feature App
Spotify began as a lightweight app with core music streaming features alone. The MVP they opted for validated that users loved instant, on-demand streaming. Over time, they have expanded with podcasts, playlists, and social features.
4. Instagram - Photo-Sharing MVP
Instagram's initial version had only photo-sharing with a filter feature. Later, it quickly attracted millions of users and evolved into a full social platform by maintaining a simple MVP.
5. SaaS MVPs for Startups
For SaaS businesses, MVPs often start as a basic dashboard or limited tool that resolves one core problem, just like analytics or team collaboration. By launching lean and collecting feedback, SaaS startups can test the pricing models, measure adoption, and scale into feature-rich platforms over time.
Types of MVP Startups Can Build
There are two main types of MVPs that startups can build: Low-Fidelity MVPs and High-Fidelity MVPs.
Low Fidelity MVPs
These types of MVPs are quick and can be used to perform inexpensive experiments. i.e., it helps you test if people are interested in your idea before building a fully-featured product. This often involves creating a basic prototype using materials like paper, wireframes, and sketches.
The goal of this type of MVP is to support validating the actual demands and check if the problem is worth solving. It works best for very early-stage startups that want to know the real interest in their idea. Here are the layers of low-fidelity MVPs:
1. Landing Page MVP
It is a simple webpage that explains your idea and is useful to find out signups or interest before building anything.
- Best For: To test the demand quickly and validate the value proposition.
- Pros: Very fast, cheap, and gives a real signal when it is useful to the users.
- Cons: It will not test the functionality. It looks overpromising and leads to a bad perception.
2. Explainer Video MVP
It is all about a short, simple video that shows how the product works.
- Best For: When the story and visual persuasion matter. To share with investors and early adopters.
- Pros: Visually engaging & helps communicate vision clearly.
- Cons: No hands-on usage & has limited feedback on usability.
3. Email MVP Test
It is an MVP used to send emails that describe your product idea or new features to a selected user group and see their interest.
- Best For: Useful if you have an existing audience or can reach potential users directly.
- Pros: Minimal or no development cost. Offers direct feedback.
- Cons: Users may ignore the emails and have less behavioural data.
4. Fake Door
It is all about showing a feature UI that leads to nowhere or to a Coming Soon page to test the interest.
- Best For: This helps find the demand for a feature before building it.
- Pros: Low effort & cost. It helps prioritize features.
- Cons: There is no actual feature behind it. Thus, users may feel misled or frustrated.
5. Crowdfunding Style MVP
It is all about presenting the product idea on crowdfunding platforms. Thus, it supports collecting pre-orders or pledges.
- Best For: It works for hardware or ambitious product ideas. Offers early revenue + demand proof.
- Pros: Raises early funds and validates market fit.
- Cons: Hard to deliver and has high expectations. It comes with the risk of public failure.
6. Wireframes
It uses sketches, clickable mockups, and mock interfaces without fully featured functionality.
- Best For: Works for usability tests, understanding UX flow, and UI feedback.
- Pros: It helps test the design, flow, and early usability, and has low development costs.
- Cons: Not fully functional and does not capture the backend performance.
High-Fidelity MVPs
- Goal: It can be used to test usability, gather customer feedback, and refine the product through MVP app development for startups and MVP design and testing.
- Best For: Startups that want to invest some time and resources to validate how people actually use the product.
Here are the layers of High-fidelity MVPs
1. Single Feature MVP
It is used to build one core feature that is extremely functional, while it ignores the rest of the features initially.
- Best For: It best works when you are very confident of which problem to solve first and want depth over breadth.
- Pros: Supports deep insights into usage. Has simpler development.
- Cons: Users may expect more initially and can feel too limited. Difficult to scale features at a later stage.
2. Minimum Lovable Product
It is more like a single-feature MVP. But it also has a polished UI/UX to delight users.
- Best For: Works well for competitive markets and first impression & retention matters.
- Pros: Builds loyalty at an early stage and offers stronger user adoption.
- Cons: Requires more design effort. Costlier and involves risk to overbuild before validating features.
High-Fidelity Prototype
It has a polished, interactive mockup that looks and offers the feel of the final product.
- Best For: Testing usability, flows, and design before real development.
- Pros: Offers great design feedback and lets you validate the look and feel. It is good for investor demos.
- Cons: It is not functional, expensive, and the user behaviour differs from the real product.
Concierge MVP
It involves behind-the-scenes manual work, but the service looks automated to users. It lets you guide users personally.
- Best For: It works for service-based ideas or when automation is complex or involves risks.
- Pros: It lets you learn exactly how people want to use it. Involves fewer technical constraints and is flexible.
- Cons: It is hard to scale and labour-intensive.
Wizard of Oz MVP
It hides manual parts entirely, like Concierge, and thus users will think it is automated.
- Best For: It works when you want to test behaviour without building infrastructure.
- Pros: It supports testing without higher development and reveals how users behave.
- Cons: It is expensive to maintain manually. Involves risks if users discover the illusion, and it seems misleading or overpromised.
Piecemeal MVP
It uses existing tools or components to stitch together a working product. You may consider using WordPress, existing platforms, and off-the-shelf APIs.
- Best For: It is helpful if you want something that works, but want to minimize custom software development.
- Pros: It saves time and delivers functionality faster. It even uses the existing tools.
- Cons: It has less control and may feel less custom. It may have technical debt and have possible limitations.
How to Pick the Right MVP Type?
Amongst all these MVP types, you may have to decide and choose the right MVP for startups. The things to consider when choosing it include:
1. Your goal right now - Check if you are validating demand, testing UI, or checking functionality.
2. Resources You have - Choose the one based on the time, money, and design or development skills.
3. Audience accessibility - Get to know if you already have users or email lists, or you can show mockups to people.
4. Risk & Expectations - Ensure that it is fine when underdelivered, and if you can manage expectations.
The Core Features Your MVP Needs to Validate Product-Market Fit
A successful MVP doesn't build everything at once. Rather, it builds only what your early users truly need. The essentials below will help you prioritize the core features that ensure validation and faster time-to-market.
MVP Validation Essentials:
- A clear value proposition that users can understand instantly.
- One core feature that solves the primary user problem.
- Simple UX that ensures easy onboarding.
- Basic analytics to track user behaviour.
- Scalable and secured backend architecture.
- Smooth performance with essential integrations only.
The AI-first MVP: Testing Features Without Breaking the Bank
At present, many startups are “AI-first”, but building a custom large language model or complex AI infrastructure from day one can be slow and break the bank. The key is to validate your AI MVP development ideas before investing heavily into tech or data science.
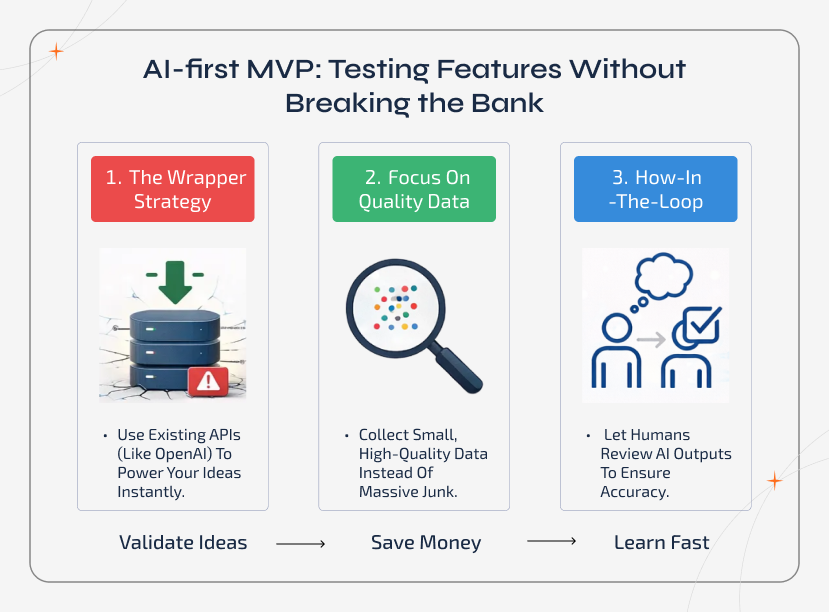
The Wrapper Strategy
Instead of building your own AI form the scratch, be smart and use APIs like OpenAI or open -source models via Hugging Face to simulate your product’s intelligent features. This lets you test the core value your AI delivers without any heavy infrastructure.
Focus on Quality, Not Quantity
AI MVPs at early stages don’t need massive datasets. So, collect high-quality and niche data that’s actually relevant to your unique solution. This will possibly power your future algorithms and ensure meaningful results.
Human-in-the-Loop
Don’t stress yourself at the start just because your AI software development isn’t perfect. Let the real people review and validate the responses during the MVP stage for startups. This keeps things accurate, builds user trust, and gives you the real feedback you need to improve the development.
Development Cost of MVP for Startup Companies
How to build an MVP for your startup without overspending is one of the most commonly asked questions among founders. The truth is, the cost of MVP software development depends on various factors, and getting to know them helps startups plan better. Key Factors That Affect MVP Development Cost Include:
1. Scope & Features
The addition of more and more features will increase the custom software development cost. A minimum viable product strategy will work best when you focus on building only the must-have features that solve the core problem.
2. Design Complexity
Opting for a simple, functional UI will cost you less when compared to a polished, custom-designed interface. Besides, the early-stage product development should prioritize usability over perfection.
3. Tech Stack
The cost factor and timeline vary based on different technologies, such as native, cross-platform software, or web frameworks. If scalability is a concern, choosing the right tech stack is important.
4. Development Team Model
The cost of building an MVP for startups varies based on hiring freelancers, building an in-house team, or partnering with a software development agency.
| Option | Cost | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freelancers & Outsourcing | Low | Budget-friendly, flexible hiring | Inconsistent quality & timelines, communication gaps | Small MVP experiments, idea validation |
| In-house Team | High | Full control, direct collaboration | Most expensive, time-consuming to hire & manage | Funded startups needing long-term control |
| MVP Development Company | Medium | End-to-end experts (developers, designers, strategists), faster delivery, less risk | Higher upfront cost than freelancers | Early-stage startups seeking reliable, scalable MVP development |
FYI - A well-scoped MVP can cost anywhere between $10,000 and $50,000+ based on the project complexity. However, starting with a lean agile MVP development approach keeps costs under control while letting you test the market instantly.
MVP Development Timeline - How Long Does it Take?
Many times, start-ups look for a quick launch. However, the timelines vary based on the goals and complexity. With agile MVP development, start-ups can validate ideas faster without sacrificing quality.
| MVP Type | Timeline | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Fidelity MVP | 2 - 4 weeks | Landing page, explainer video |
| High-Fidelity MVP | 6 - 12 weeks | An app with a core feature |
| SaaS MVP | 8 - 14 weeks | Subscription dashboards |
A realistic MVP timeline will include Discovery & feature planning, MVP design& usability testing, Lean development in sprints, Launch to early adopters, and Iterative improvements.
MVP Launch Strategy - Soft Launch vs Beta vs Public Release
It is possible to find out how quickly you will gain real insights based on your MVP launch approach. The table below will clarify the same in a better way:
| Strategy | Best For | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Soft Launch | Early validation | Controlled audience, low-risk testing |
| Closed Beta | Iteration phase | Real feedback from engaged testers |
| Public Launch | Strong demand validated | Fast traction, revenue potential |
So, you shall start small, measure, and then scale it up. This lays the solid foundation for a successful MVP launch strategy.
Moreover, validating an MVP is not only about users, but also about the market size. Startups should understand whether the market is wide enough to scale before investing in development. And this is exactly where market sizing sets its foot. In sizing, TAM (Total Addressable Market) defines the total market demand, SAM (Serviceable Available Market) shows the reachable market, and SOM (Serviceable Obtainable Market) represents the realistic early share a startup can capture.

Quick Insights!
Common Myths Founders Get Wrong
📜 An MVP is not a beta product. A beta is for testing performance, while MVP is for validating the problem.
📜 An MVP is not a MMP (Minimum Marketable Product). MMP focuses on selling, while an MVP focuses on learning and validation.
📜 An MVP is still be viable and reliable. Even with limited features, it works properly for real users and delivers real value.
Tools & Platforms to Use for Rapid MVP Prototyping
In order to speed up the early-stage product development, start-ups can use no-code & low-code tools as they help with faster iterations. Check out the respective tools to use for different MVP prototyping stages:
- Prototype or Design - Figma, Adobe XD.
- Mobile App MVP - FlutterFlow, Bravo Studio.
- Web App MVP - Webflow, Bubble, Wix Welo.
- Backend & Authentication - Firebase, Supabase.
- Payment Integration - Razorpay, Stripe.
How to Measure MVP Success
Tracking the right KPIs will give you a clear picture of whether your idea is worth scaling. With the structured analytics and feedback loops, start-ups and businesses can make data-backed decisions instantly.
Important MVP Validation Metrics:
- Activation rate
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
- Retention rate or churn score
- Feature adoption rate
- Time-to-value (TTV)
- User satisfaction score (NPS)
- Revenue per user (ARPU) for SaaS MVPs
Common & Costly Mistakes in Native vs Cross-Platform App Development Decisions
Despite developing a strong minimum viable product strategy, many startups find it difficult to handle the repeating mistakes. Avoiding these pitfalls will save time, money, and effort in your MVP development journey.
1. Adding too many features too soon - An MVP should solve one core problem. Adding additional features will slow down the development and dilute the focus.
2. Skipping real user feedback - Building features with one opinion is always risky. Early testing and iteration are the backbone of the MVP design and testing.
3. Complex engineering of the product - Often, startups waste resources due to complex designs or heavy tech stacks. It is essential to stick to lean, agile MVP development.
4. Ignoring market validation - It is essential to validate before scaling as a polished product without demand leads to failure of the MVP.
5. Failing to plan for scalability - While MVPs should be lean, selecting a tech stack that allows growth will help avoid expensive rebuilds at a later stage.
By paying attention to these mistakes, startups can ensure their MVP app development efforts lead to quick validation, lower risks, and long-term success.
Common Challenges in MVP Development for Startups
Building an MVP is the most approachable process any startup can make. However, it does come with challenges. In most cases, the early-stage founders struggle to balance between keeping it simple and making it really valuable for real-time users. Let us take a look at the most common challenges in MVP development for startups:
1. Balancing Features & Simplicity
The idea behind a minimum viable product strategy is to focus on the most required features. However, many startups end up overbuilding too many features even during the initial stages. This results in increasing the costs, delaying the launch, and weakening the clarity of the value proposition.
2. User Adoption Risks
Although the MVP is built very well, there is no guarantee that the users will embrace it. Early adopters will find it too limited or may not fully understand the product. Overcoming this requires a clear onboarding process and continuous feedback loops during the MVP design and testing.
3. Choosing the Right MVP Launch Strategy
Decide whether you are willing to launch the product to a small test group or go big from day one. Selecting the wrong approach will lead to wasted resources or missed insights. For startups, a phased launch with agile iterations will usually work.
4. Scaling from MVP to Full Product
An MVP is not just the end goal. It is just the starting point. Many founders underestimate the effort required to turn an MVP into a scalable product. Tech debt, architecture upgrades, and additional features development will slow down the growth when there is no proper planning.
Secret Tips to Overcome MVP Development Challenges
Despite getting to know the challenges, it is essential to find ways to overcome the MVP development challenges to stay on the safer side.
1. Focus on One Core Feature
It is better not to build every feature at once. Instead, you should focus on identifying one most important problem your product solves and build it. As a result, the development process takes less time, reduces cost, and helps you validate your idea faster.
2. Let Real User Feedback Guide You
Rather than relying on just assumptions, startups can focus on launching the MVP to a small group of users and observe how they actually use it. Their feedback will represent what works, what will not work, and the features that are truly needed. This saves time and prevents startups from building features that nobody wants, saving time and effort.
3. Adopt Agile MVP Development
It is better to break the entire development into small, iterative cycles. Focus on releasing updates quickly, testing them, and improving the features based on results. Agile MVP development ensures you are always moving closer to product-market fit rather than wasting months on launching big.
4. Plan Early for Scalability
Besides keeping the MVP lean, it is vital to choose the right tech stack. To stay away from the obstacles to MVP development, selecting the flexible, scalable technologies in the early stage prevents bottlenecks when the product grows. Thus making it easier to move from MVP to a full-featured product without major rebuilds.
How to Make Your MVP Successful for Startups - Expert Insights
Building an MVP is not just about speed; it is all about focusing, validation, and scalability. By following proven principles, startups can reduce the risks, attract early users, and accelerate growth.
Focus on Solving One Core Problem
The best of MVPs will not be doing everything at once. Rather, they work on solving the single biggest problem users face. With this as a focus, startups can deliver real value faster and avoid spending too many resources on less useful features.
Use Lean Startup MVP Principles
It is good to adapt to the build-measure-learn cycle. i.e., it involves creating a simplified version to release it quickly and thereby gather insights from users to use that data to improve the feature. With this approach, startups can stay away from MVP software development challenges while ensuring they are always moving towards the actual product-market fit.
Prioritize Speed with Agile MVP Development
With agile approaches, it is possible to break the process into small, manageable sprints. This not only offers faster delivery but also the flexibility to adapt to user feedback. Besides, it comes with quicker iterations compared to traditional development.
Partner with an MVP Development Company
Collaborating with experts will save several months of trial and error. An experienced MVP development company provides proven frameworks, tech expertise, and domain knowledge that speed up the development process, starting from idea to launch.
Build for Scalability from Day One
Although an MVP is a minimal version, it should be designed in such a way that it can scale anytime. For this, it is vital to choose the right architecture and tech stack at an early stage. This ensures the startups don't have to face expensive rebuilds when user demand increases.
Post-MVP Roadmap - From Beta to Scalable Product
Launching an MVP is just the beginning. The real process begins after validation. Hence, start-ups need a clear roadmap to turn their MVP into a fully-functioning, high-performing, market-ready product.
Here is how we at Sparkout help start-ups scale:
- We refactor your MVP architecture to handle more users without downtime or expensive rework at any point later.
- We build what users need truly by analysing behaviour, feedback, and adoption patterns.
- With automation, we reduce manual operations to increase speed, reduce costs, and boost user experience.
- We safeguard your product as usage and data needs evolve.
- We optimize monetization models and execute GTM strategies to accelerate customer acquisition and brand trust.
With Sparkout as your technology partner, your MVP evolves from a working prototype into a scalable, future-ready product with a strong competitive edge.
From MVP to MLP: Make Users Hooked Up
In the upcoming days, launching a product that merely works won’t make any changes. To stand out from competitors, your MVP should be something unique that keeps users coming back and talking about your app. This is the jump from Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to Minimum Lovable Product (MLP).
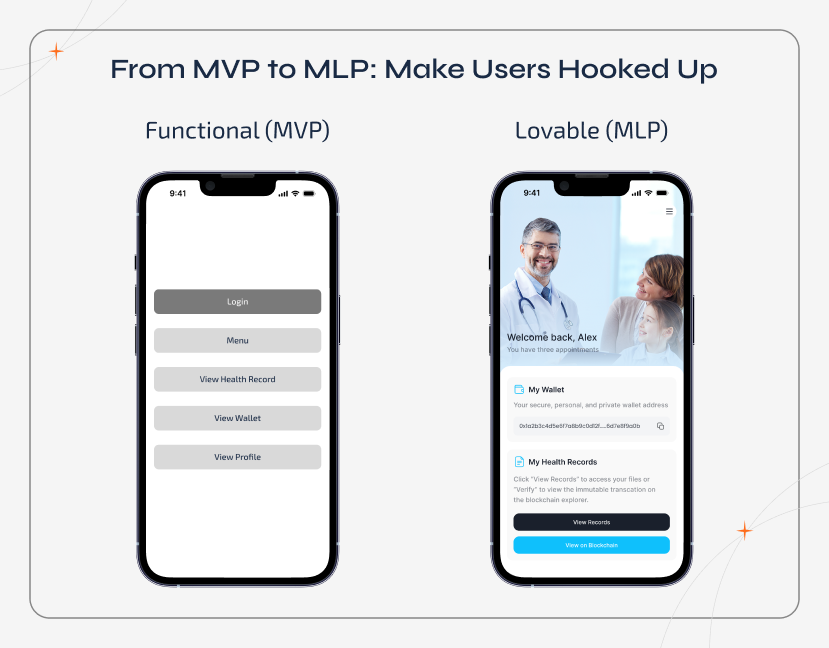
The Emotional Hook
Identify that one specific feature that makes users genuinely enjoy your product. It can be a lightning-fast response, smooth animation, or personalized greeting. Always remember to add small details that make them smile and remember your brand.
Micro-Interactions Matter
Do not underestimate tiny little UX details, because they could be a life changer. Things like subtle hover effects, smart notifications, and intuitive swipe gestures can make a $10 MVP feel like a polished $100 product. These details build trust and create emotional connections between your brand and users.
Retention Over Acquisition
Early success isn’t just about getting sign-ups, it’s more about keeping the users engaged. Monitor whether the users return, how they interact, and how seamlessly they complete tasks. A lovable MVP builds loyalty, not just traffic.
Iterate With Love
Gather feedback from a couple of early users and see what they actually enjoy. Use those insights to enhance features that resonate, remove friction points, and make your product feel thoughtful at every touchpoint.
Why Choose Sparkout for Building an MVP for Startups?
At Sparkout, we offer minimum viable product development services to help startups turn ideas into market-ready MVPs with speed, scalability, and clarity. With a proven track record, faster delivery, and startup-friendly pricing, we deliver lean MVPs that reduce risks, validate assumptions, and offer long-term growth.
1. Proven Track Record & Global Experience
Sparkout has worked with over 150+ clients globally and delivered 240+ projects since 2017. With this level of experience, it is possible for the team to easily find the startup challenges and what succeeds or fails when it comes to real MVPs.
2. Strong, Multi-Disciplinary Team
With over 100+ experts in different domains & technologies covering frontend, backend, AI/ML, blockchain, Sparkout has the talent in-house. The experts can develop your MVP with advanced AI features, sleek UI, or secure backend systems.
3. Startup-Friendly & Cost-Transparent Approach
Sparkout offers pricing and engagement models that are suitable for building an MVP for Startups. With the transparent and cost-effective pricing structure, startups need not worry about getting any charges later.
4. Lean & Agile Methodologies
By following lean startup principles and the agile MVP development for Startups, the Sparkout team focuses on the most impactful features to release first, gather feedback, and iterate.
5. Strong Capability for Scalability & Quality Assurance
Sparkout uses scalable architectures and modern tech stacks and offers quality assurance. It helps startups lay a strong foundation, and thus, you need not rebuild from scratch later.
6.Industry Versatility
With experience in diverse industries from fintech, education, blockchain, logistics, and ecommerce, our custom software development company delivers MVPs based on your domain by understanding the design, UX constraints, and regulatory requirements.
7. End-to-End Services
Sparkout offers discovery, strategy, prototyping, UI/UX design, development, MVP launch, ongoing feedback analysis, and scalability support. The team not only works to deliver the MVP but also helps the startups grow.
Winding Up - Turning MVP into a Scalable Product
An MVP is a strategic tool with which a startup can validate ideas, reduce risks, and get faster time-to-market. It is all about focusing on the right features by getting insights from real users and following an agile MVP development process. With this, startups can redefine a simple idea into a product that offers long-term scalability.